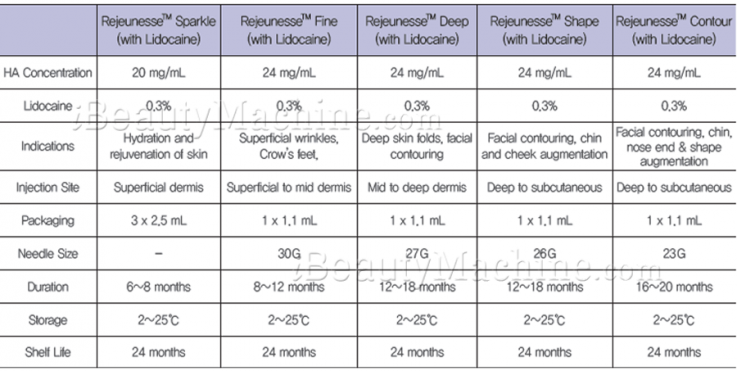
The concentration of hyaluronic acid (HA) in dermal fillers varies greatly based on the product and how it is meant to be used. The amount of HA present in a filler determines its viscosity, flexibility, duration of action, and appropriateness for certain facial locations. The primary variations in HA concentration seen in dermal fillers are summarized as follows:
1. Low HA Concentration Fillers
HA Concentration: Typically lower, ranging from 10-20 mg/mL.
Texture: These fillers are usually softer and more fluid.
Use Case: Best suited for fine lines, superficial wrinkles, and areas requiring minimal volume augmentation, such as the under-eye area or fine lip lines.
Longevity: Generally shorter-lasting (approximately 6-9 months) due to quicker absorption by the body.
Brands with Low HA concentration on our website:
2. Medium HA Concentration Fillers
HA Concentration: Moderate concentration, usually around 20-25 mg/mL.
Texture: More viscous and elastic than low concentration fillers.
Use Case: Ideal for moderate wrinkles, nasolabial folds, lip enhancement, and mild volumizing.
Longevity: Medium duration (about 9-12 months), providing a balance between fluidity and volumizing effects.
Brands with Medium HA concentration on our website:
3. High HA Concentration Fillers
HA Concentration: Higher concentration, often ranging from 25-30+ mg/mL.
Texture: Thicker, more robust, and provides more structural support.
Use Case: Suitable for deeper wrinkles, significant volume loss, cheek augmentation, jawline contouring, and areas requiring substantial lift or support.
Longevity: Longer-lasting (12-18 months or more), due to slower degradation.
4. Ultra High HA Concentration Fillers
HA Concentration: Very high, sometimes exceeding 30 mg/mL.
Texture: Very dense and cohesive, offering maximum lift and projection.
Use Case: Used for significant volume restoration in areas like the cheeks, chin, or jawline where strong structural support is required.
Longevity: Can last up to 18-24 months, depending on the product and individual factors.
Additional Factors Influenced by HA Concentration
Cross-Linking: The filler's characteristics are also influenced by the degree of cross-linking in the HA molecules. Depending on the cross-linking method employed, fillers with the same HA concentration might have varying textures and durations.
Viscosity and Cohesiveness: Greater lift and structure can be achieved with thicker, more viscous fillers that may feel stiffer to the touch due to higher HA concentrations.
Hydrophilicity: HA is hydrophilic, meaning it attracts water. Fillers with higher HA concentrations can absorb more water, potentially increasing the final volume post-injection.
Conclusion
The targeted cosmetic outcome, the treated region, and the individual requirements of the patient all influence the choice of HA concentration in a dermal filler. Greater doses are employed for more significant volume restoration and facial sculpting, whereas lower concentrations are best for sensitive areas or small adjustments.